The influence of surface texture and roughness on shear and compressive forces in tribological applications is analyzed using numerical simulations and taking into account the geometry of real surface elements. Topographic data of the representative surface structures are generated with high spatial resolution using an optical interference method. The three-dimensional velocity field in the lubricating film is calculated using the Lattice Boltzmann method for laminar flows of Newtonian fluids. The pressure and shear flow factors are determined from this velocity field by comparison with the Reynolds differential equation. This approach allows an efficient determination of the hydrodynamic parameters of microstructured surfaces. In particular, the influence of production-related anisotropies of the surface textures on the hydrodynamic load-bearing capacity and friction is recorded. The results show that detailed numerical simulations are suitable for efficiently and accurately calculating the characteristic properties of tribological lubricating films and can thus contribute to a better understanding and prediction of EHD problems.
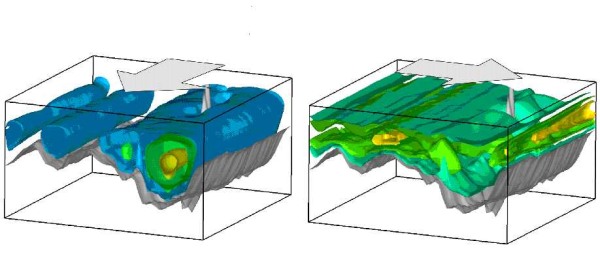
Detail of the isosurfaces of the velocity component in the flow direction for the pressure flow on the crankshaft element with anisotropic surface roughness. Left: Axial flow, right transverse to anisotropic structures.
Publications
- G. Brenner, A. Al-Zoubi: Determination of Lubrication Characteristics of Bearings using the lattice Boltzmann Method, to appear in Proceedings of the Parallel CFD Conference, Washington, 2005.
- G. Brenner, A. Al-Zoubi, M. Mukinovic, H. Schwarze, S. Swoboda, Numerical Simulation of Surface Roughness Effects in Laminar Lubrication using the lattice-Boltzmann Method, Journal Tribology, submitted.
- H. Schwarze , S. Swoboda, G. Brenner , A. Al-Zoubi, M. Mukinovic, Numerical Simulation of Surface Roughness Effects in Laminar Lubrication using the lattice Boltzmann Method, Tribology and Lubrication Technology, 2006, accepted for publication.